Stone, minerals and semiprecious of the world stone
Sulphate: Barite -->rus
 Diagnostic cart.
Diagnostic cart.
Ba SO4
Crystal structure rhombic
Specific unit weight 4,48
Cleavage perfect absolute
Fracture, break padman
Colors colourless, polycoloured (multicoloured)
Colors in powder triturate white
Glance (glitter, glare) from glass to mother-of-pearl
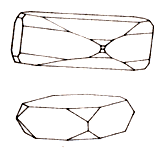
 Barite rarely is presented the isolated crystals. Often meetings, the very rich in verges crystals of barytes have a prismatic look with characteristic completion as a "chisel". Usually they are transparent and colourless, but can also be white or painted in various colors (honey mead-yellow is typical, gold, pink, rose and azure sky-blue). Rarely there are independent crystals; much more frequent they are incorporated in Druses, sometimes truly magnificent.
Barite rarely is presented the isolated crystals. Often meetings, the very rich in verges crystals of barytes have a prismatic look with characteristic completion as a "chisel". Usually they are transparent and colourless, but can also be white or painted in various colors (honey mead-yellow is typical, gold, pink, rose and azure sky-blue). Rarely there are independent crystals; much more frequent they are incorporated in Druses, sometimes truly magnificent.
Barite is a colourless or white mineral consisting of barium sulphate in orthorhombic crystalline form, occurring in sedimentary rocks and with sulphide ores: a source of barium. Formula: BaSO4. Also called: barytes, heavy spar.
Basic ore of barium; filling compound is in rubber and paper industry; suspensoid at the boring drilling and other Form of crystals. Quite often there are beautiful many-sided crystals; mainly plate tablet lamellar, rarer prismatic crystals. Crystalline structure. Anionic complex [SO4]2 - with Ba. Class of symmetry. Rhombo-bipyramidal group- mmm. Cleavage. Perfect (from cleavage of Calcite differs a direct corner between planes); mineral forms the Cleavage pricking out on a rhombic prism. Aggregates. Grainy, radiant, dense, kidney-shaped reniform, tabular, continuous.
Diagnostic indication.
Perfect cleavage on a parallelepiped, insolubility and absence of boiling up at a contact with acids, mainly, it is allowed quickly to recognize large weight barytes. It has glassy brilliance with a tendency to mother-of-pearl and easily scratches a knife. Crack and melt fuse only on the edges of thin fragments, painting flame in a yellow-green color (characteristic for a barium). In a powdery kind slowly dissolves in the concentrated sulphuric acid; from addition of water solution cloud from the fall of BaSO4.
Origin provenance genesis.
Barite be found mainly in hydrothermal deposits, either actually barytes or containing barytes in composition a gangue in which it forms an association with ore sulfates. This mineral can also be in veins and voids in rock among limestones and dolomites. Usually barytes forms vast in size dense or grainy opaque accumulations of white color.
Deposit minefield mine field occurrence subsoil.
Main deposits within the limits of Italy, where the industrial booty of barytes goes, located in the areas of Trentino-Alto-Adidje (mine of Darso) and Sardinia. In the past barytes was developed in industrial scales in Val'sasine (Kortabbio, province of Komo), in the foot-hills of Alps in the provinces of Bergamo, Breshia and Venice. Druses and magnificent crystals found in the mineries of Brosso and Traversella in an area P'emont and in the area of Perzhine-vetriolo in Trentino. Large yellow crystals acted from the mine of Barega near-by Niksusa (Sardinia). Elegant Druses of crystals discovered in other places of this island, sometimes slightly bluish, which are highly valued collectors. The supplies of barytes are celled in deposits mine, stratiforms and remaining types. About 55% confirmed supplies abroad concentrated in vein, lode, mine deposits. Leading world producer of barytes are China, USA, India and Kazakhstan.

Use, practical application, deployment.
Barite is basic mineral raw material for the receipt preparation of barium. Ground barytes is used as a pigment in paper industry and for making of paints, and also as a suspensoid of clay borings solutions, in-use at driving of oil-wells. The sulfate of barium is used in medicine as a mean of diagnostics at sciagraphy research of digestive highway. Basic technological properties, determining the wide spectrum of the industrial use of barytes, are a high closeness, chemical sluggishness, low hardness (small abrasivity), ability to take in x-ray photography radiation, large maintenance of barium, whiteness.
A barium is an element of main sub-group of the second group, sixth period of the periodic system of chemical elements, with an atomic number 56. Designated character of Ba (lat. Barium). Simple matter a barium is a soft, malleable alkaline-earth metal of silvery-white color. Possesses high chemical activity. In nature in a native kind does not almost meet.





Barite, or a heavy spar is a sulfate of barium. Glance (glitter, glare) mother-of-pear nacreous to glass. Transparent to translucent. Colors: greyish-white, yellow, rose; rarer is colourless, aquatic-transparent. A line is white. Fracture, break uneven, step. Fragile. Cleavage perfect absolute. Paints flame in a green color. Appears in hydrothermal ore vein, lode, mines. Crystals (rhombic Crystal structure) are plate tablet lamellar, columnar, basaltiform, fissile (in this case they quite often accrete in wall outlets - "barytes roses").
By a side by side with this continuous the masses are typical - grainy, dense, downlow. Used as a suspensoid of borings solutions, in medicine, and also for protecting from radiations, as filler and as a polishing mean. Places of distribution: North Rhine-Vestfaliya, Garc, Shvarcval'd, Odenval'd (Germany), Garc (Germany), Karintiya (Austria), Switzerland, England, USA, CIS.

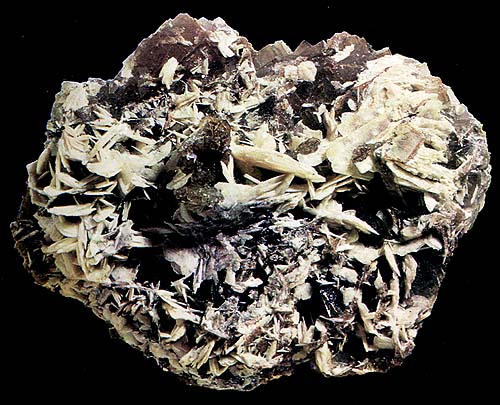
Barite, calcium rhodochrosite is in a shell, in swamp ore. Kar'er"e", Kerch mine. A shell 7х5 sm. A photo: © A.A. Evseev.

Barite. Sferolit (2,5 sm ) is in a shell (Ca-rhodochrosite). Kerch. 1980th. A photo: © V.A. Slyetov
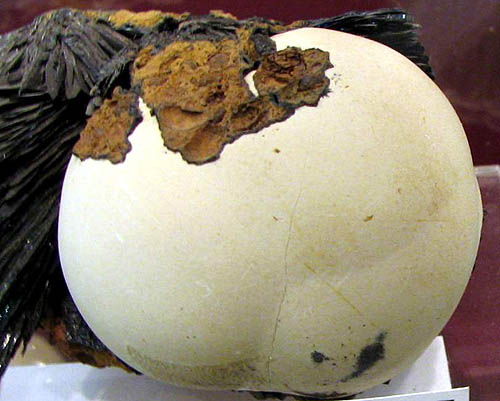
Barite, vivianite. Kerch mine, Crimea, Ukraine, CIS. A photo: © A.A. Evseev.

Barite (light), fluorite (violet). Berbes, Asturiya, Spain (EU)
A barium is needed: at ischemic heart trouble, chronic coronarism, diseases of organs of digestion. Makes a making more a compact action on tissues, and this action is used for treatment of the hypertrophied glands. Homoeopaths recommend to accept a carbonate barium elderly people, by suffering obesity, when the symptoms of sclerosis of cerebral vessels are present, and also at cardiovascular diseases (hypertensive illness, аортит, aneurysm), diseases of respiratory tracts (adenoids, chronic tonsillitis, bronchitis, recurrent, relapsing quinsies) and digestive highway (gastritises, flatulence, diarrhoeas, locks).
Food sources of barium: marine inhabitants are able to accumulate a barium from surrounding water, thus in concentrations, in 7-100 (and for some marine plants - to 1000) times, exceedings his maintenance in salt water (laminaria). It is set that at ischemic heart trouble, chronic coronarism, diseases of organs of digestion maintenance of barium goes down in tissues. The table of contents of barium in the organism of people makes an about 20 mg.
The symptoms of poisoning a barium are similar. Gipertenziya, premature reductions of ventricles of heart, ventricular tachycardia, fibrillation of ventricles and asystole. Marked expirations from eyes, mydriasis, sialosis, nausea, vomiting. Sickliness of abdominal wall, diarrhea, violation of act of swallowing. Myshechnye fibrillation, speeded up breathing, was swollen lights, tonic, clonic cramps and paralysis. Kaliopenia and hypophosphatemia, metabolic acidosis and glucopenia. A barium is attributed to the toxic microelements, however ignores a mutagene or carcinogenic.
Basic displays of surplus of barium: muscular spasms, disorders of co-ordination of motions and cerebral activity; abundant salivation, nausea, vomiting, colics, diarrhea, dizziness, sonitus, pallor of skin covers, abundant death-damp; weakness of pulse, bradycardia, brachycardia, bradyrhythmia, extrasystole, beats. Even in insignificant concentrations a barium is rendered by the expressed influence on smooth muscles (in small concentrations weakens them, causes reduction - in large). Compounds of barium reduce permeability of the potassium ductings.
DOPOG #4.3 

Matters substances, which select flammable gases at a contact with water
Risk of fire and explosion at a contact with water.
Gruz, which had scattered, it is necessary to cover and hold dry
Sine-blue rhombus, number of DOPOG, black or white flame
DOPOG #5.1 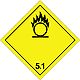
Matters substances, which oxidize
Risk of stormy reaction, self-ignition or explosion at a contact with combustible or flammable matters
To shut out formation of mixture of load with flammable or combustible matters (for example by sawdusts)
Yellow rhombus, number of DOPOG, black flame above by a circle
DOPOG #6.1 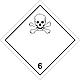
Toxic non biological matters substances (toxin)
Risk of poisoning at inhalation, contact with a derma or swallowing. Make a danger for a water environment or sewage system
To use a mask for emergency abandonment of transport vehicle
White rhombus, number of DOPOG, black skull and crossed cross-bones
DOPOG #8 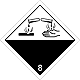
Corrosive (caustic, pungent, acrid) substances matters
Risk of burns as a result of eating away of derma. Can stormily react between itself (components), with water and other matters. Matter, that spilled / scattered, can select a corrosive pair.
Make a danger for a water environment or sewage system
White overhead half of rhombus, black - lower, isometric, number of DOPOG, test tubes, hands
 DOPOG #1
DOPOG #1 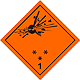
Bomb which explode bursts
Can be characterized in a number of properties and effects, such as: by critical mass; by variation of fragments; intensive fire/thermal heat stream; bright flash; loud noise or smoke.
Sensitiveness to the shoves and/or shots and/or heat
To use shelter, here to repose on safe distance from windows
Orange sign, image of bomb at an explosion
DOPOG #4.2 
Matters substances, apt at spontaneous combustion
Risk of fire as a result of spontaneous combustion in case if packing is damaged or the source of maintenance happened.
Can stormily react with water
White overhead half of rhombus, red - lower, isometric, number of DOPOG, black flame
| Наименование особо опасного при транспортировке груза | Номер ООН | Класс ДОПОГ |
| БАРИЙ | 1400 | 4.3 |
| Барий азотнокислый БАРИЯ НИТРАТ | 1446 | 5.1 |
| Барий бромистый Бария бромид | 1564 | 6.1 |
| Барий бромнуватистий БАРИЯ БРОМАТ | 2719 | 5.1 |
| Барий углекислый Бария карбонат | 1564 | 6.1 |
| Барий двохромовокислий Бария дихромат | 3087 | 5.1 |
| Барий марганцовокислый БАРИЯ ПЕРМАНГАНАТ | 1448 | 5.1 |
| Барий серный Бария сульфид | 1564 | 6.1 |
| Барий хлорист Бария хлорид | 1564 | 6.1 |
| БАРИЯ АЗИД УВЛАЖНЕН с массовой долей воды не менее 50% | 1571 | 4.1 |
| БАРИЯ АЗИД сухой или увлажненный с массовой долей воды менее 50% | 0224 | 1 |
| БАРИЯ БРОМАТ | 2719 | 5.1 |
| Бария бромата моногидрат БАРИЯ БРОМАТ | 2719 | 5.1 |
| Бария бромид | 1564 | 6.1 |
| Бария гидратокис Бария гидроксид | 2923 | 8 |
| Бария гидрид | 3134 | 4.3 |
| Бария гидроксид | 2923 | 8 |
| БАРИЯ ГИПОХЛОРИТ, который содержит более 22% активного хлора | 2741 | 5.1 |
| Бария дихромат | 3087 | 5.1 |
| Бария карбонат | 1564 | 6.1 |
| БАРИЯ НИТРАТ | 1446 | 5.1 |
| БАРИЯ ОКИСЕЛ | 1884 | 6.1 |
| БАРИЯ ПЕРМАНГАНАТ | 1448 | 5.1 |
| БАРИЯ ПЕРОКСИД (перекись) | 1449 | 5.1 |
| БАРИЯ ПЕРХЛОРАТ ТВЕРДЫЙ | 1447 | 5.1 |
| БАРИЯ ПЕРХЛОРАТУ РАСТВОР | 3406 | 5.1 |
| Бария сплавы непирофорные твердые токсические, которые опасно реагируют с водой | 3134 | 4.3 |
| БАРИЯ СПЛАВЫ ПИРОФОРНЫЕ | 1854 | 4.2 |
| БАРИЯ СОЕДИНЕНИЕ, Н.З.К. | 1564 | 6.1 |
| Бария сульфид | 1564 | 6.1 |
| БАРИЯ ХЛОРАТ ТВЕРДЫЙ | 1445 | 5.1 |
| БАРИЯ ХЛОРАТА РАСТВОР | 3405 | 5.1 |
| Бария хлорид | 1564 | 6.1 |
| Бария хлорид | 1564 | 6.1 |
| Бария хлорид, раствор | 3287 | 6.1 |
| Бария хромат | 1564 | 6.1 |
| БАРИЯ ЦИАНИД | 1565 | 6.1 |
